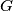
is a set of non-constant functions
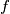
. Each
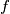
is defined on the real line and has the form
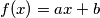
for some real
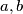
. If
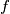
and
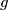
are in
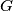
, then so is
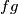
, where
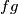
is defined by
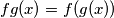
. If
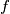
is in
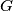
, then so is the inverse
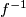
. If
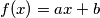
, then
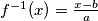
. Every
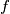
in
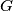
has a fixed point (in other words we can find
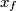
such that
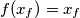
. Prove that all the functions in
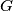
have a common fixed point.
%V0
$G$ is a set of non-constant functions $f$. Each $f$ is defined on the real line and has the form $f(x)=ax+b$ for some real $a,b$. If $f$ and $g$ are in $G$, then so is $fg$, where $fg$ is defined by $fg(x)=f(g(x))$. If $f$ is in $G$, then so is the inverse $f^{-1}$. If $f(x)=ax+b$, then $f^{-1}(x)= \frac{x-b}{a}$. Every $f$ in $G$ has a fixed point (in other words we can find $x_f$ such that $f(x_f)=x_f$. Prove that all the functions in $G$ have a common fixed point.
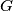 is a set of non-constant functions
is a set of non-constant functions 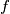 . Each
. Each 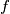 is defined on the real line and has the form
is defined on the real line and has the form 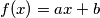 for some real
for some real 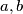 . If
. If 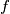 and
and 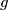 are in
are in 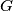 , then so is
, then so is 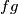 , where
, where 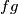 is defined by
is defined by 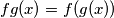 . If
. If 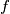 is in
is in 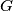 , then so is the inverse
, then so is the inverse 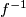 . If
. If 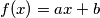 , then
, then 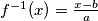 . Every
. Every 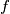 in
in 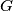 has a fixed point (in other words we can find
has a fixed point (in other words we can find 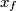 such that
such that 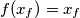 . Prove that all the functions in
. Prove that all the functions in 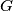 have a common fixed point.
have a common fixed point.  Školjka
Školjka