A set 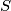 of points from the space will be called completely symmetric if it has at least three elements and fulfills the condition that for every two distinct points
of points from the space will be called completely symmetric if it has at least three elements and fulfills the condition that for every two distinct points 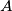 and
and 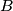 from
from 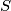 , the perpendicular bisector plane of the segment
, the perpendicular bisector plane of the segment 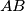 is a plane of symmetry for
is a plane of symmetry for 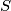 . Prove that if a completely symmetric set is finite, then it consists of the vertices of either a regular polygon, or a regular tetrahedron or a regular octahedron.
. Prove that if a completely symmetric set is finite, then it consists of the vertices of either a regular polygon, or a regular tetrahedron or a regular octahedron.
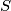 of points from the space will be called completely symmetric if it has at least three elements and fulfills the condition that for every two distinct points
of points from the space will be called completely symmetric if it has at least three elements and fulfills the condition that for every two distinct points 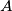 and
and 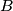 from
from 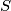 , the perpendicular bisector plane of the segment
, the perpendicular bisector plane of the segment 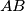 is a plane of symmetry for
is a plane of symmetry for 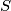 . Prove that if a completely symmetric set is finite, then it consists of the vertices of either a regular polygon, or a regular tetrahedron or a regular octahedron.
. Prove that if a completely symmetric set is finite, then it consists of the vertices of either a regular polygon, or a regular tetrahedron or a regular octahedron.  Školjka
Školjka