For any integer 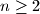 , we compute the integer
, we compute the integer 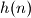 by applying the following procedure to its decimal representation. Let
by applying the following procedure to its decimal representation. Let  be the rightmost digit of
be the rightmost digit of 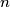 .
.
If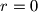 , then the decimal representation of
, then the decimal representation of 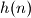 results from the decimal representation of
results from the decimal representation of 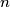 by removing this rightmost digit
by removing this rightmost digit 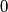 .If
.If 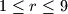 we split the decimal representation of
we split the decimal representation of 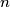 into a maximal right part
into a maximal right part 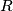 that solely consists of digits not less than
that solely consists of digits not less than  and into a left part
and into a left part 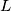 that either is empty or ends with a digit strictly smaller than
that either is empty or ends with a digit strictly smaller than  . Then the decimal representation of
. Then the decimal representation of 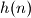 consists of the decimal representation of
consists of the decimal representation of 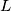 , followed by two copies of the decimal representation of
, followed by two copies of the decimal representation of 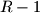 . For instance, for the number
. For instance, for the number 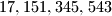 , we will have
, we will have 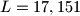 ,
, 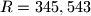 and
and 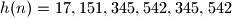 .Prove that, starting with an arbitrary integer
.Prove that, starting with an arbitrary integer 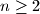 , iterated application of
, iterated application of 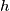 produces the integer
produces the integer 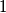 after finitely many steps.
after finitely many steps.
Proposed by Gerhard Woeginger, Austria
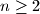 , we compute the integer
, we compute the integer 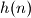 by applying the following procedure to its decimal representation. Let
by applying the following procedure to its decimal representation. Let  be the rightmost digit of
be the rightmost digit of 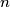 .
.If
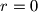 , then the decimal representation of
, then the decimal representation of 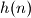 results from the decimal representation of
results from the decimal representation of 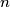 by removing this rightmost digit
by removing this rightmost digit 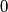 .If
.If 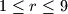 we split the decimal representation of
we split the decimal representation of 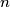 into a maximal right part
into a maximal right part 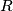 that solely consists of digits not less than
that solely consists of digits not less than  and into a left part
and into a left part 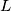 that either is empty or ends with a digit strictly smaller than
that either is empty or ends with a digit strictly smaller than  . Then the decimal representation of
. Then the decimal representation of 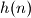 consists of the decimal representation of
consists of the decimal representation of 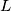 , followed by two copies of the decimal representation of
, followed by two copies of the decimal representation of 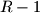 . For instance, for the number
. For instance, for the number 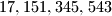 , we will have
, we will have 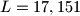 ,
, 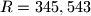 and
and 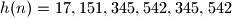 .Prove that, starting with an arbitrary integer
.Prove that, starting with an arbitrary integer 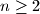 , iterated application of
, iterated application of 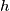 produces the integer
produces the integer 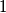 after finitely many steps.
after finitely many steps.Proposed by Gerhard Woeginger, Austria
 Školjka
Školjka