Slični zadaci
Let 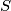 be the set of all pairs
be the set of all pairs 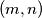 of relatively prime positive integers
of relatively prime positive integers 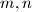 with
with 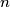 even and
even and 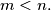 For
For 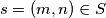 write
write 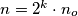 where
where 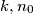 are positive integers with
are positive integers with 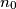 odd and define
odd and define 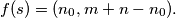 Prove that
Prove that 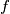 is a function from
is a function from 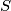 to
to 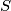 and that for each
and that for each 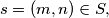 there exists a positive integer
there exists a positive integer 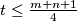 such that
such that 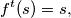 where
where 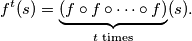
If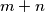 is a prime number which does not divide
is a prime number which does not divide 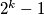 for
for 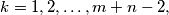 prove that the smallest value
prove that the smallest value 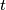 which satisfies the above conditions is
which satisfies the above conditions is ![\left [\frac{m+n+1}{4} \right ]](/media/m/8/7/8/878d7261cbd40fe8c838d36d2b94fea7.png) where
where ![\left[ x \right]](/media/m/8/4/7/847a3b7449538c2b99179a2953e7f9e0.png) denotes the greatest integer
denotes the greatest integer 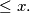
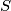 be the set of all pairs
be the set of all pairs 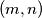 of relatively prime positive integers
of relatively prime positive integers 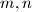 with
with 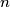 even and
even and 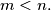 For
For 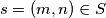 write
write 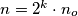 where
where 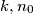 are positive integers with
are positive integers with 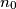 odd and define
odd and define 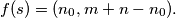 Prove that
Prove that 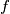 is a function from
is a function from 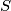 to
to 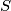 and that for each
and that for each 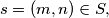 there exists a positive integer
there exists a positive integer 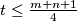 such that
such that 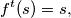 where
where 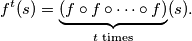
If
 is a prime number which does not divide
is a prime number which does not divide 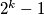 for
for 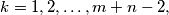 prove that the smallest value
prove that the smallest value 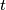 which satisfies the above conditions is
which satisfies the above conditions is ![\left [\frac{m+n+1}{4} \right ]](/media/m/8/7/8/878d7261cbd40fe8c838d36d2b94fea7.png) where
where ![\left[ x \right]](/media/m/8/4/7/847a3b7449538c2b99179a2953e7f9e0.png) denotes the greatest integer
denotes the greatest integer 
 Školjka
Školjka  of positive integers into itself is defined by the equality
of positive integers into itself is defined by the equality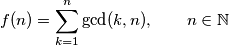
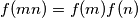 for every two relatively prime
for every two relatively prime 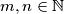 .
.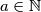 the equation
the equation 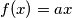 has a solution.
has a solution.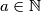 such that the equation
such that the equation  and
and  be non-negative integers such that
be non-negative integers such that 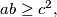 where
where  is an integer. Prove that there is a number
is an integer. Prove that there is a number 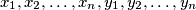 such that
such that 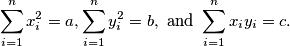
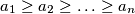 be real numbers such that for all integers
be real numbers such that for all integers 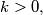
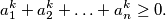
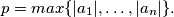 Prove that
Prove that 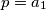 and that
and that 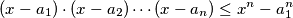 for all
for all 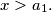
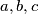 be positive integers satisfying the conditions
be positive integers satisfying the conditions 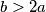 and
and 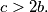 Show that there exists a real number
Show that there exists a real number 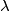 with the property that all the three numbers
with the property that all the three numbers 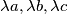 have their fractional parts lying in the interval
have their fractional parts lying in the interval ![\left(\frac {1}{3}, \frac {2}{3} \right].](/media/m/c/f/e/cfe91f93cf6950a9edc579467b2af1f5.png)
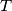 denote the set of all ordered triples
denote the set of all ordered triples 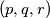 of nonnegative integers. Find all functions
of nonnegative integers. Find all functions 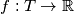 satisfying
satisfying 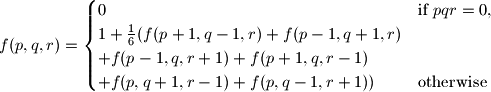
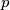 ,
, 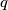 ,
,  .
. 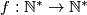 satisfying
satisfying 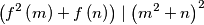
 and
and 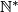 stands for the set of all positive integers:
stands for the set of all positive integers: 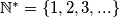 .
. 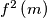 , we mean
, we mean 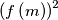 (and not
(and not 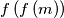 ).
).