Point 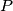 lies on side
lies on side 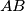 of a convex quadrilateral
of a convex quadrilateral 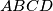 . Let
. Let 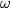 be the incircle of triangle
be the incircle of triangle 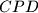 , and let
, and let 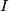 be its incenter. Suppose that
be its incenter. Suppose that 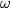 is tangent to the incircles of triangles
is tangent to the incircles of triangles 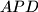 and
and 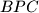 at points
at points 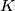 and
and 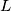 , respectively. Let lines
, respectively. Let lines 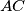 and
and 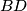 meet at
meet at 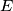 , and let lines
, and let lines 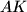 and
and 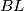 meet at
meet at 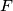 . Prove that points
. Prove that points 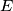 ,
, 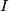 , and
, and 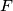 are collinear.
are collinear.
Author: Waldemar Pompe, Poland
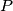 lies on side
lies on side 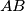 of a convex quadrilateral
of a convex quadrilateral 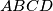 . Let
. Let 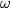 be the incircle of triangle
be the incircle of triangle 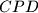 , and let
, and let 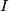 be its incenter. Suppose that
be its incenter. Suppose that 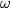 is tangent to the incircles of triangles
is tangent to the incircles of triangles 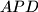 and
and 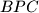 at points
at points 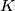 and
and 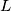 , respectively. Let lines
, respectively. Let lines 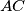 and
and 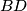 meet at
meet at 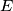 , and let lines
, and let lines 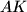 and
and 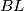 meet at
meet at 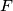 . Prove that points
. Prove that points 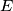 ,
, 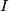 , and
, and 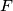 are collinear.
are collinear. Author: Waldemar Pompe, Poland
Slični zadaci
The incircle 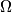 of the acute-angled triangle
of the acute-angled triangle 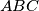 is tangent to its side
is tangent to its side 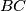 at a point
at a point 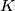 . Let
. Let 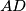 be an altitude of triangle
be an altitude of triangle 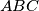 , and let
, and let 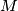 be the midpoint of the segment
be the midpoint of the segment 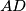 . If
. If 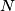 is the common point of the circle
is the common point of the circle 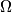 and the line
and the line 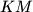 (distinct from
(distinct from 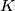 ), then prove that the incircle
), then prove that the incircle 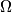 and the circumcircle of triangle
and the circumcircle of triangle 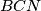 are tangent to each other at the point
are tangent to each other at the point 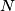 .
.
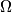 of the acute-angled triangle
of the acute-angled triangle 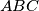 is tangent to its side
is tangent to its side 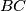 at a point
at a point 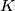 . Let
. Let 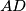 be an altitude of triangle
be an altitude of triangle 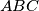 , and let
, and let 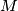 be the midpoint of the segment
be the midpoint of the segment 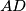 . If
. If 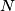 is the common point of the circle
is the common point of the circle 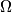 and the line
and the line 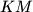 (distinct from
(distinct from 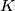 ), then prove that the incircle
), then prove that the incircle 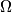 and the circumcircle of triangle
and the circumcircle of triangle 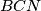 are tangent to each other at the point
are tangent to each other at the point 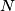 .
. In a triangle 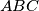 , let
, let 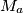 ,
, 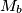 ,
, 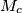 be the midpoints of the sides
be the midpoints of the sides 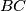 ,
, 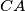 ,
, 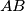 , respectively, and
, respectively, and 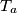 ,
, 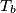 ,
, 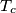 be the midpoints of the arcs
be the midpoints of the arcs 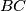 ,
, 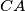 ,
, 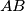 of the circumcircle of
of the circumcircle of 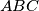 , not containing the vertices
, not containing the vertices 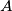 ,
, 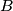 ,
, 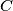 , respectively. For
, respectively. For 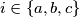 , let
, let 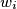 be the circle with
be the circle with 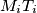 as diameter. Let
as diameter. Let 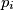 be the common external common tangent to the circles
be the common external common tangent to the circles 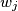 and
and 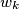 (for all
(for all 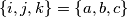 ) such that
) such that 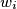 lies on the opposite side of
lies on the opposite side of 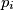 than
than 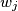 and
and 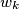 do.
do.
Prove that the lines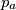 ,
, 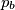 ,
, 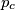 form a triangle similar to
form a triangle similar to 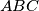 and find the ratio of similitude.
and find the ratio of similitude.
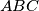 , let
, let 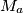 ,
, 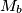 ,
, 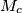 be the midpoints of the sides
be the midpoints of the sides 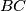 ,
, 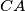 ,
, 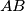 , respectively, and
, respectively, and 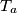 ,
, 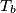 ,
, 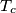 be the midpoints of the arcs
be the midpoints of the arcs 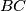 ,
, 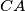 ,
, 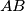 of the circumcircle of
of the circumcircle of 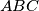 , not containing the vertices
, not containing the vertices 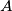 ,
, 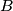 ,
, 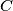 , respectively. For
, respectively. For 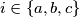 , let
, let 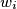 be the circle with
be the circle with 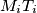 as diameter. Let
as diameter. Let 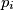 be the common external common tangent to the circles
be the common external common tangent to the circles 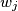 and
and 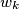 (for all
(for all 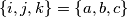 ) such that
) such that 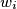 lies on the opposite side of
lies on the opposite side of 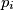 than
than 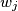 and
and 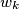 do.
do. Prove that the lines
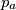 ,
, 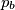 ,
, 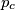 form a triangle similar to
form a triangle similar to 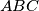 and find the ratio of similitude.
and find the ratio of similitude. Let 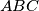 be a fixed triangle, and let
be a fixed triangle, and let 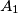 ,
, 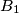 ,
, 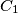 be the midpoints of sides
be the midpoints of sides 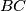 ,
, 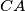 ,
, 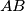 , respectively. Let
, respectively. Let 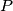 be a variable point on the circumcircle. Let lines
be a variable point on the circumcircle. Let lines 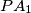 ,
, 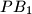 ,
, 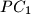 meet the circumcircle again at
meet the circumcircle again at 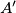 ,
, 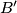 ,
, 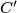 , respectively. Assume that the points
, respectively. Assume that the points 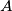 ,
, 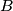 ,
, 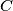 ,
, 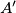 ,
, 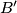 ,
, 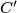 are distinct, and lines
are distinct, and lines 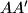 ,
, 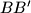 ,
, 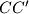 form a triangle. Prove that the area of this triangle does not depend on
form a triangle. Prove that the area of this triangle does not depend on 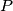 .
.
Author: Christopher Bradley, United Kingdom
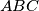 be a fixed triangle, and let
be a fixed triangle, and let 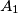 ,
, 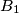 ,
, 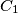 be the midpoints of sides
be the midpoints of sides 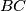 ,
, 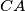 ,
, 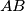 , respectively. Let
, respectively. Let 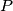 be a variable point on the circumcircle. Let lines
be a variable point on the circumcircle. Let lines 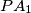 ,
, 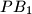 ,
, 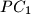 meet the circumcircle again at
meet the circumcircle again at 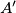 ,
, 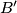 ,
, 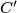 , respectively. Assume that the points
, respectively. Assume that the points 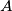 ,
, 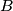 ,
, 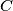 ,
, 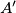 ,
, 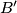 ,
, 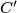 are distinct, and lines
are distinct, and lines 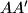 ,
, 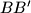 ,
, 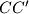 form a triangle. Prove that the area of this triangle does not depend on
form a triangle. Prove that the area of this triangle does not depend on 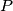 .
. Author: Christopher Bradley, United Kingdom
Determine the smallest positive real number 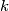 with the following property. Let
with the following property. Let 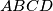 be a convex quadrilateral, and let points
be a convex quadrilateral, and let points 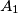 ,
, 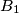 ,
, 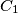 , and
, and 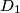 lie on sides
lie on sides 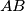 ,
, 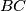 ,
, 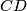 , and
, and 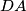 , respectively. Consider the areas of triangles
, respectively. Consider the areas of triangles 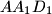 ,
, 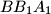 ,
, 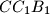 and
and 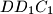 ; let
; let 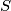 be the sum of the two smallest ones, and let
be the sum of the two smallest ones, and let 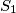 be the area of quadrilateral
be the area of quadrilateral 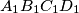 . Then we always have
. Then we always have 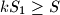 .
.
Author: unknown author, USA
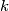 with the following property. Let
with the following property. Let 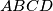 be a convex quadrilateral, and let points
be a convex quadrilateral, and let points 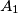 ,
, 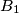 ,
, 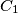 , and
, and 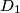 lie on sides
lie on sides 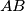 ,
, 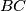 ,
, 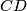 , and
, and 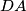 , respectively. Consider the areas of triangles
, respectively. Consider the areas of triangles 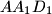 ,
, 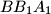 ,
, 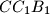 and
and 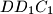 ; let
; let 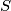 be the sum of the two smallest ones, and let
be the sum of the two smallest ones, and let 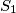 be the area of quadrilateral
be the area of quadrilateral 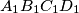 . Then we always have
. Then we always have 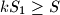 .
. Author: unknown author, USA
 Školjka
Školjka  be a variable point on the line
be a variable point on the line 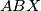 and
and 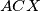 intersect at two distinct points
intersect at two distinct points 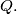 Prove that the line
Prove that the line 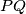 passes through a point independent of
passes through a point independent of 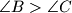 . Point
. Point 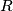 the circumradius. Point
the circumradius. Point 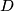 is the foot of the altitude from vertex
is the foot of the altitude from vertex 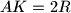 , and
, and 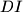 and
and 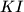 meet sides
meet sides 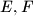 respectively. Let
respectively. Let 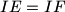 .
. 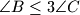 .
.